Add Feedback
This article focuses on feature explanations. For detailed API fields and limitations, please click the link above.
1. When to Add Feedback?
By using a dedicated addFeedback endpoint, you can reduce manual maintenance costs + improve memory accuracy + support continuous self-improvement.
As shown in the table below, compared to editing a specific memory, natural language feedback is more suitable for real-world business operations and non-technical user actions.
| Natural Language Feedback | Targeted Memory Editing | |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Describe issues or corrections | Directly specify a memory to edit |
| User Threshold | Low, suitable for non-technical users | Higher, typically for developers/admins |
| System Involvement | Automatic parsing, locating, and updating by the system | Manually driven updates |
| Update Scope | May affect multiple related memories | Usually impacts a single memory |
| Application Scenario | Dialog correction, expired knowledge, business rule changes | Precise revision, structured maintenance |
2. Key Parameters
- Feedback Content (feedback_content): The user’s natural language feedback on the model’s response, used to understand the needs for memory updates.
- Knowledge Base Scope (allow_knowledgebase_ids): The knowledge bases targeted by the user’s feedback, restricting which knowledge base memories may be modified.
- Conversation ID (conversation_id): The unique conversation identifier associated with the user's feedback, used to link the current feedback to its context.
3. How It Works
In a chatbot scenario, the user clicks the "feedback" button below the model's answer, fills in the feedback form, and submits.
Based on the feedback, the backend triggers a MemOS add/feedback API call to update the memory, removing the need to manually operate user memories.
- Validity Analysis: When a user submits feedback, MemOS analyzes the feedback with the conversation context to determine if it is valid and related before deciding to update the memory.
- Update Type Recognition: MemOS automatically classifies feedback-driven memory update requests into two types: keyword replacement and semantic update, based on the feedback and its contextual meaning.
- Updating Memories: According to the classification result, corresponding memory updates are executed—creating new memories or updating/conflicting/obsolete memories.
- Keyword Replacement: Searches for memory entries containing the target keywords and performs precise updates;
- Semantic Update: Generates new semantic memory based on user feedback and merges or updates related memories after retrieving them.
4. Usage Examples
Semantic Update of Knowledge Base Memory
In enterprises, it's common for corporate policies or knowledge to update, while the knowledge base isn't updated in time. Try using the simplest interaction to keep your knowledge base always current.
import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your MemOS API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "1212",
"feedback_content": "The purchase limit for office software is 600 yuan, not 800 yuan.",
"allow_knowledgebase_ids": ["idxxxxx"] # Replace with your knowledge base ID above
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/add/feedback"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(f"result: {res.json()}")
import os
import requests
import json
# Replace with your MemOS API Key
os.environ["MEMOS_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
os.environ["MEMOS_BASE_URL"] = "https://memos.memtensor.cn/api/openmem/v1"
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"conversation_id": "1211",
"query": "Please check the software purchase reimbursement quota.",
"knowledgebase_ids": ["idxxxxx"] # Replace with your knowledge base ID above
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"Token {os.environ['MEMOS_API_KEY']}"
}
url = f"{os.environ['MEMOS_BASE_URL']}/search/memory"
res = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
# Pretty print JSON output
json_res = res.json()
print(json.dumps(json_res, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
Sample (simplified) output:
"memory_detail_list": [
{
"id": "8a4f3d2e-c417-4e53-bc25-54451abd5ac8",
"memory_key": "Software Purchase Reimbursement Policy (Trial Version)",
"memory_value": "This policy aims to standardize the company's various software procurement and reimbursement processes, requiring all software purchases to adhere to the maximum amount for each category. The purchase limit for design software is 1000 yuan, suitable for graphic design, video editing, and prototyping software, such as Photoshop and Premiere. The development/code software limit is 1500 yuan, which includes IDEs and frameworks, e.g., PyCharm and Visual Studio. The office software purchase limit is 800 yuan, suitable for document editing and spreadsheets, such as Office suite and WPS. Data analysis software is limited to 1200 yuan, for statistics/visualization, e.g., Tableau, Power BI. Security/protection software limit is 1000 yuan, for antivirus/firewall. Collaboration/project management software, 900 yuan, such as Jira and Slack. Specialized industry software limit is 2000 yuan, requiring special approval. All purchases must comply with company budgeting and security requirements, and those over the limit require justification and approval.",
"memory_type": "LongTermMemory",
"create_time": 1765525947718,
"conversation_id": "default_session",
"status": "activated",
"confidence": 0.99,
"tags": [
"software purchase",
"reimbursement policy",
"approval process",
"budget",
"security",
"mode:fine",
"multimodal:file"
],
"update_time": 1765525947720,
"relativity": 0.8931847
},
{
"id": "a72a04d1-d7ba-4ebd-9410-0097bfa6c20d",
"memory_key": "Office Software Purchase Limit",
"memory_value": "User confirms the office software purchase limit is 600 yuan, not 800 yuan.",
"memory_type": "WorkingMemory",
"create_time": 1765531700539,
"conversation_id": "1212",
"status": "activated",
"confidence": 0.99,
"tags": [
"purchase",
"office software",
"budget"
],
"update_time": 1765531700540,
"relativity": 0.7196722
}
]
In the Console - Knowledge Base, all details of knowledge base memories corrected or supplemented through natural language are displayed.
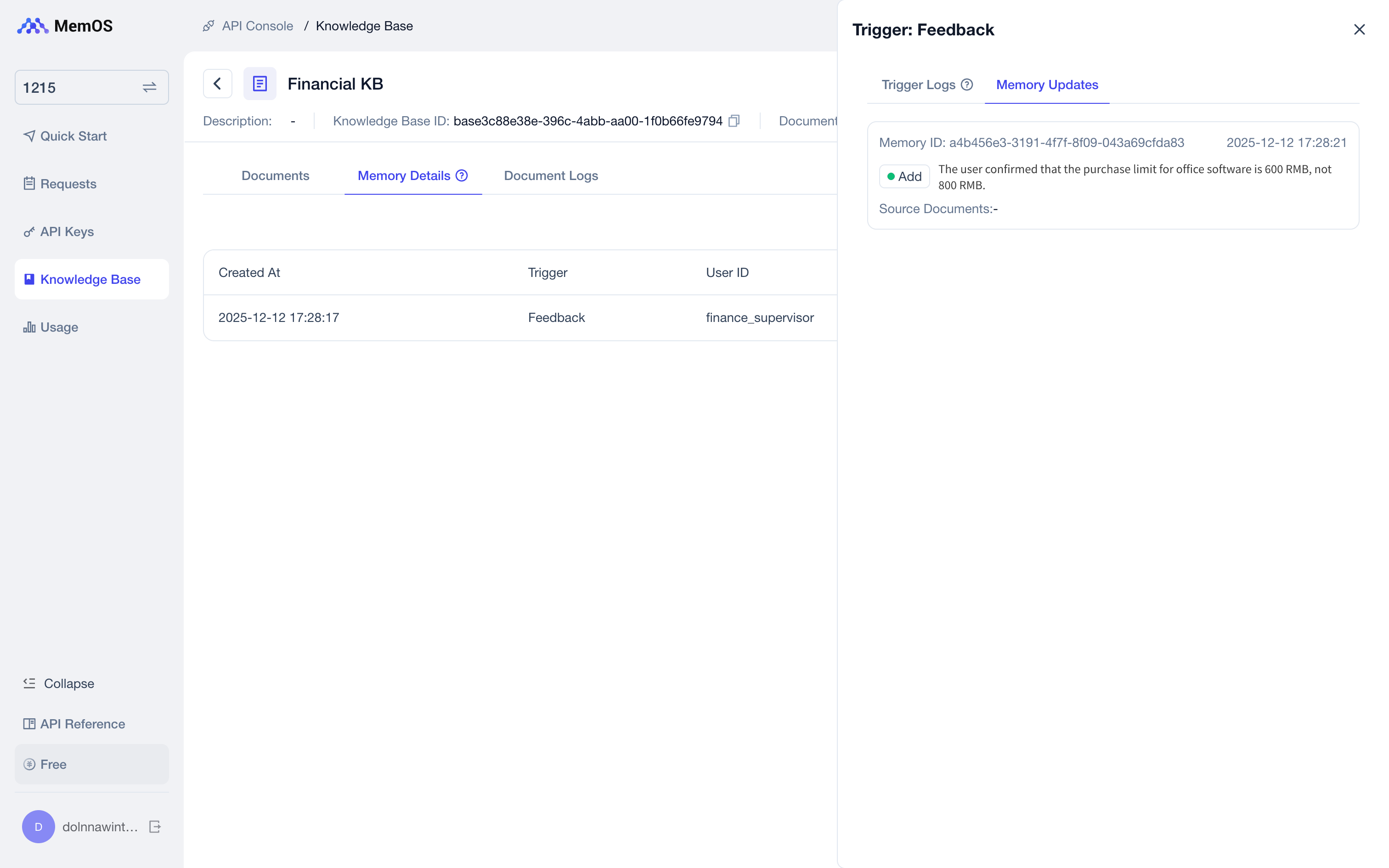
Keyword Replacement Memory
As shown below, besides updating semantic memories, MemOS also supports describing direct word replacements—where no conversation ID (conversation_id) is needed.
data = {
"user_id": "memos_user_123",
"feedback_content": "I have changed my name. Please replace 'User 1' with 'User 2' everywhere.",
"allow_knowledgebase_ids": ["123", "456"]
}